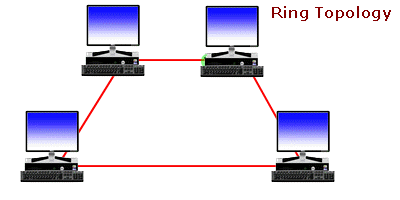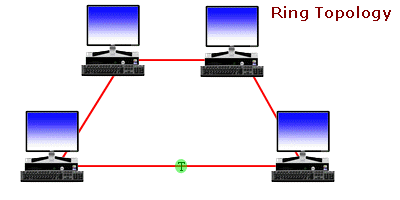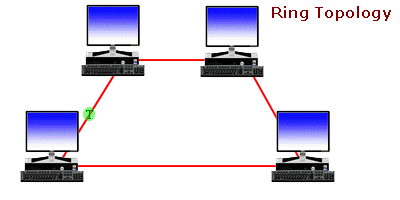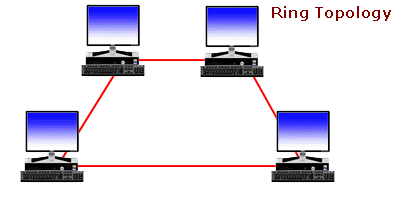
1. Definition of Computer
Computer is an electronic data processing device, which accepts data and instructions, process the data according to given instructions and produces the desired results to the user.
1.1.1 Computer Science
It is the study of the various parts of computer systems such as Hardware, Software and humans who use them, as well as the society and organization in which they are used.
1.1.2 Characteristics of Computer
-
Speed:
Computer is capable of doing arithmetic and logical calculations with rapid speed [in nano seconds]. The speed of the computer can be measured in millions of instructions per second (MIPS)
-
Accuracy:
100 % error free results by its process
-
Storage & retrieval:
Large amount of data / Information can be recorded, stored, and retrieved in future in faster way.
-
Diligence:
Computers can be used for continuous processes
-
Versatility:
It can be used for various works such as Office automation, worksheet calculations, engineering drawing etc.,
1.1.3 Applications of Computers
-
Mission control and Simulation:
Computers can be used to mission control like airplanes (auto pilot), rackets, and satellites. And computers are also used for simulations of different models of planes, ships, and vehicles before they are going to manufacture.
-
Engineering applications:
For the purpose of Computerized design and drafting and Machine or CAD / CAM and for various engineering applications
-
Accounting and Statistics:
For the purpose of accounting process such as invoices, Inventory, Pay bill and statistical calculations.
-
Medicine:
To record and maintenance of Patients/Staff/Inventory databases and Preparation of different scanning/analysis reports.
-
Education:
Giving of Computer based Teaching and Training [CBT] and providing computerized library for articles and publications.
-
Entertainment:
Using it as an entertainment device for listening music, watching video and pictures and playing of games.
1.1.4. History of computers
-
The calculi: Unknown origin
-
The Abacus:From 2600 BC
-
Calculating machines:Babbage and Byron in 1800s
-
Theory of computation:During 1936
-
Programmable computers Aiken, 1944 and ENIAC, 1946
-
Store program computers:Von Newmann, 1945 and EDSAC, 1949
-
Before 1976:Mostly mainframe computers, Very large computers and Very expensive computers
-
First microcomputer:Apple Computer Inc, 1976
-
processor 8086: IBM PC revolution, 1981 and Speed > 1000 Mhz, 2001
1.1.5. Generation of Computers
First Generation Computers (1940-1956)
- Were vacuum tube based machines
- Used magnetic drums for memory
- Input was based on punched cards and paper tape
- Output was displayed on printouts
- Relied on binary coded language (language of 0s and 1s) to perform operations
- Examples : ENIAC, EDVAC and UNIVAC
- Computation time was milliseconds
- Were very large, and required a lot of space for installation
- Were non-portable
- Were very expensive to operate and used a large amount of electricity
Second Generation Computers (1960s)
- Were based on transistor technology
- Used magnetic drums/tapes for memory
- Input was based on keypads
- Used printed displays/seven segment display screens for output
- Relied on assembly and binary coded languages
- Computation time was in microseconds
- Smaller than first generation computers
- Were movable
- Less expensive than first generation computes
Third Generation Computers ( 1964 to early 1970s)
- Were based on integrated circuit technology
- Used magnetic disks for memory
- They were able to reduce computational time from microseconds to nanoseconds.
- They were easily portable and more reliable than the second generation
- The size of these computers were smaller as compared to previous computers.
- Extensive use of high-level languages became possible
- Commercial production became easier and cheaper.
Fourth Generation computers ( from late 1970s)
- Were microprocessor based systems
- Were based on VLSI (very Large Scale Integrated Ci rcuits) technology
- Using mass storage device for memory
- These computes are very small
- They are portable and quite reliable
- Interconnection of computers leads to better communication and resource sharing
- The production cost is very low
- Cheapest among all the other generations
Fifth Generation Computers
Up to fourth generation, the classification was based purely on hardware. Fifth generation computers
are classified based on software also. VLSI technology is used in fifth generation computers. They have
large main memories. The speed is also high. In addition to all, this fifth generation computers run
software called „expert systems‟.
|